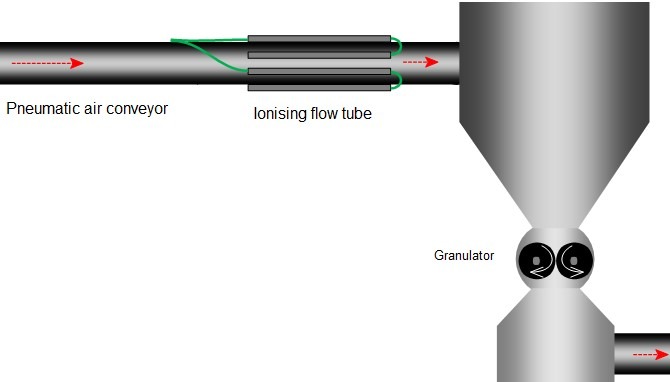
Waste transfer ionising flow-tube
PROBLEM
Waste materials such as end trim is transported via ducting, entering the air bleed off chamber (cyclone), which allows the waste product to drop into the granulator.
Static charges built up on the waste material cause it to stick to the walls of the cyclone, which when heavy enough to overcome the static bond, drops jamming the granulator.
SOLUTION
Introducing ionisation into the airflow minimise the waste build up on the cyclone walls preventing it dropping in large clumps.
An ionising flow tube is one answer to this problem where large ducting is part of the system carrying large quantities of waste material.
Download
